India is celebrating “Azadi Ka Amritkal” wherein we are developing a new and prosperous India that is determined to become a developed country by 2047. To reach this objective, one of the most important milestones is to ensure financial inclusion for everyone in the country. This financial inclusion is critical because it provides an avenue for the poor for bringing their savings into the formal financial system and remit money to their families in villages besides protecting themselves from the clutches of the usurious money lenders.
Not only this, it helps the government to deliver appropriate financial services at an affordable cost on a timely basis to vulnerable groups such as low-income groups and weaker sections who lack access to even the most basic banking services, especially during a crisis. Thus, financial inclusion is an enabler to achieve equitable and inclusive growth of the nation.
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
In order to promote accessible banking services, particularly among low-income segments of society, a significant financial inclusion initiative called the “Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana” was launched in 2014. This groundbreaking initiative aimed to provide a bank account to every household and ensure affordable access to financial services, thereby facilitating the goal of inclusive banking for all. The key focus areas of this scheme are:
- Universal access to banking services – Branch and BC
- Basic savings bank accounts with overdraft facility of Rs. 10,000/- to every eligible adult
- Financial Literacy Programme– Promoting savings, use of ATMs, getting ready for credit, availing insurance and pensions, using basic mobile phones for banking
- Creation of Credit Guarantee Fund – To provide banks some guarantee against defaults
- Insurance – Accident cover up to Rs. 1,00,000 and life cover of Rs. 30,000 on account opened between 15 Aug 2014 to 31 January 2015
- Pension scheme for Unorganized sector
Since the inception of “Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana,” more than 46.25 crore beneficiaries have opened accounts with a deposit balance amounting to Rs. 1,73,954 crore. Out of these numbers, 67% accounts have been opened in rural or semi-urban areas and 56% account holders are women which clearly reflects the success of this initiative
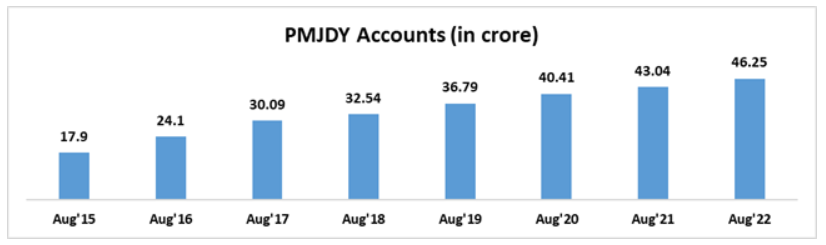
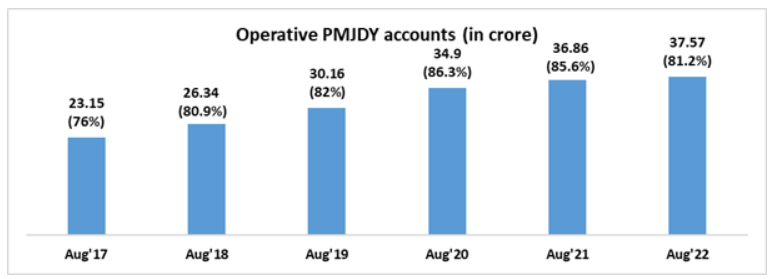
Another success factor of this scheme is that out of these 46.25 crores Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) accounts, 37.57 crores (81.2%) are operative which means there are customer-induced transactions in these accounts.
These high operability numbers for Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) accounts indicate that the targeted end-customers which in this case were the marginalized sections of society have been able to understand financial operations and conduct them without difficulties.
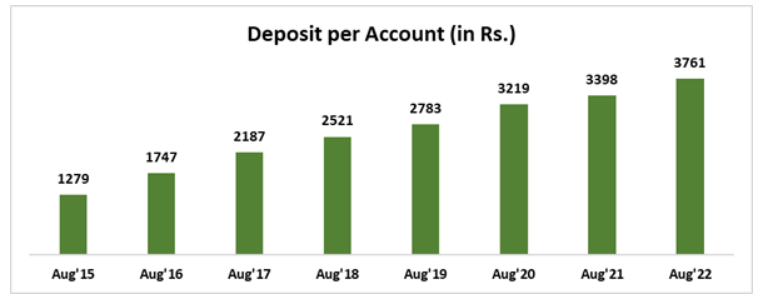
Not only this, average deposit per account has increased over 2.9 times from Aug’15 that indicates the increased usage of accounts and inculcation of saving habit among account holders which has been a remarkable success in empowering and providing financial security to the weaker sections of the society.
This “Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana,” was further enhanced in 2018 with:
- Focus shift from ‘Every Household’ to ‘Every Unbanked Adult’
- RuPay Card Insurance – Free accidental insurance cover on RuPay cards increased from Rs. 1 lakh to Rs. 2 lakh for PMJDY accounts opened after 28.8.2018.
- Enhancement in overdraft facilities
- OD limit doubled from Rs 5,000/- to Rs 10,000/-; OD upto Rs 2,000/- (without conditions).
- Increase in upper age limit for OD from 60 to 65 years
Furthermore, to leverage the huge potential for cards penetration offered by Indian market and boost retail payments in India, RuPay card was launched by NPCI (National Payments Corporation of India) for Indian consumers, merchants, and banks. The RuPay card is not only safe and secure but also cost effective as transaction processing happens domestically which leads to lower cost of clearing and settlement for each transaction.
The government data as on August 2022 shows that 32.8 million RuPay cards have been issued to PMJDY accountholders and their usage has increased over time. To enhance the coverage of PMJDY accounts to more people, Jan Dhan Darshak’s mobile app was launched to identify villages that were not served by banking touchpoints within 5 km. These villages were allocated to various banks on a high-priority basis so that more people can benefit from this initiative and there has been a significant decrease in such villages.
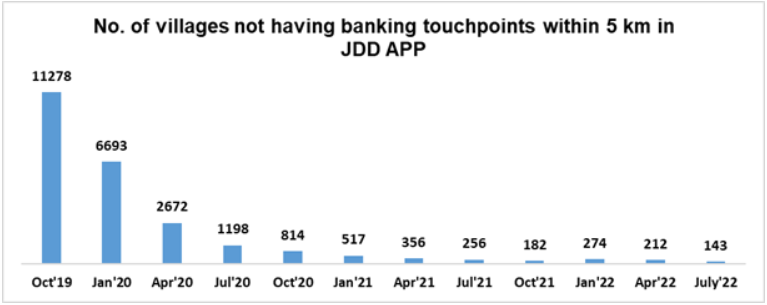
This initiative has been recognized as the world’s most far-reaching initiative towards financial inclusion and has laid down the foundation of government’s people-centric economic initiatives. This was clearly visible during covid-19 times when through DBT (Direct Bank Transfer), within 10 days of nationwide lockdown more than about 20 crore women PMJDY accounts were credited with ex-gratia as covid-19 financial assistance.
Not only this, in PM-KISAN, increased wages under MGNREGA were directly transferred to the beneficiaries through these accounts. The biggest advantage of these accounts has been that it ensures every rupee reaches its intended beneficiary without any system leakage so marginalized section of the society was provided immediate relief with the help of these accounts.
“Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana” has been successfully implemented as a biggest program of Financial Inclusion to include people who were deprived of even rudimentary financial services. This has brought in transformational as well as directional change and has built in a new Financial Inclusion ecosystem that is capable of delivering financial services to the marginalised sections of the society and ensuring an inclusive growth in the country.
Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY)
The Prime Minister Narendra Modi-led government places a strong emphasis on inclusive prosperity, as evidenced by the launch of impactful schemes like the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) in 2015. This visionary initiative is designed to provide comprehensive support to small and micro-entrepreneurs by offering collateral-free micro-credit of up to Rs. 10 lakhs.
By facilitating easy access to credit, PMMY fosters innovation, elevates per capita income, and empowers economically disadvantaged individuals. Since its inception in 2015 until March 2023, an impressive amount of Rs. 23.2 lakh crore has been sanctioned across 40.82 crore loan accounts under PMMY. These loans have served as a catalyst for economic growth and have played a significant role in driving entrepreneurship and job creation in the country.
Notably, 68% of these accounts belong to women entrepreneurs, highlighting the government’s focus on empowering women and promoting gender equality. Additionally, 51% of the accounts are owned by entrepreneurs from marginalized communities, including Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST), and Other Backward Classes (OBC). This demonstrates the government’s commitment to uplifting these sections of society and promoting inclusive development.
Pradhan Mantri Street Vendor’s Atmanirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi)
The government is dedicated to supporting job creation and entrepreneurship through effective measures. In the employment sector, the government has established an integrated system to streamline opportunities. To enhance financial inclusion among street vendors, the government introduced the PM SVANidhi scheme, emphasizing self-employment and empowerment.
This micro-credit scheme has rapidly gained momentum, delivering over 42.87 lakh loans amounting to Rs. 5,182 crore to 45.32 lakh beneficiaries in two tranches over the past two years. To address the financial inclusion of street vendors and empower them economically, the government introduced the Pradhan Mantri Street Vendor’s Atmanirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme.
This initiative focuses on the principles of ‘Swarozgar’ (self-employment), ‘Svavlamban’ (self-reliance), and ‘Swabhimaan’ (dignity). By providing street vendors with access to credit, the scheme aims to uplift their socio-economic status and enable them to establish sustainable livelihoods.
The PM SVANidhi scheme has emerged as one of the fastest-growing micro-credit initiatives by the Government of India. It has successfully delivered over 42.87 lakh loans, amounting to an impressive Rs. 5,182 crore, to 45.32 lakh beneficiaries across two tranches in the last two years. This significant achievement demonstrates the scheme’s effectiveness in supporting street vendors and enabling them to build their businesses.
Through the PM SVANidhi scheme, street vendors receive collateral-free working capital loans, allowing them to access funds for inventory, infrastructure development, and working capital requirements. This financial support helps them expand their operations, enhance the quality of their goods and services, and improve their overall business sustainability.
Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM)
The Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM) has played a pivotal role in driving socio-economic transformation in rural areas by mobilizing over eight crore women into 82 lakh Self Help Groups (SHGs). These SHGs serve as catalysts for rural economic empowerment as they provide women with a collective platform to undertake income-generating activities and develop entrepreneurial skills.
The mobilization of women into SHGs under DAY-NRLM has ushered in a wave of positive change, leading to improved access to financial services, enhanced livelihood opportunities, and increased socio-economic empowerment. By pooling resources, sharing knowledge, and collectively engaging in income-generating activities, women in SHGs have been able to overcome socio-economic barriers and unlock their entrepreneurial potential.
One of the significant impacts of DAY-NRLM has been the fostering of financial inclusion among rural women. By organizing themselves into SHGs, women gain access to formal banking services, microcredit, and other financial products. This access to financial services has not only helped them meet their immediate financial needs but has also enabled them to save, invest, and plan for their future.
The efforts of the Indian government in breaking barriers and promoting financial inclusion have not only expanded access to financial services but also created a more inclusive and resilient economy. By ensuring that the underprivileged have equal opportunities to participate in the formal financial system, India has taken significant strides towards reducing poverty by assisting 25 crore people out of multi-dimensional poverty in last 10 years, fostering entrepreneurship, and enhancing social welfare.
As India continues on its journey towards financial inclusion, sustained efforts are required to address the evolving needs of the population. This includes leveraging technology to provide digital financial services, expanding the reach of banking infrastructure to remote areas, and promoting financial literacy and education. By strengthening these foundations, India can build a more equitable and prosperous society where every individual has the opportunity to fulfill their economic aspirations.
References
https://financialservices.gov.in/new-initiatives/schemes
https://web.umang.gov.in/landing/department/pradhan-mantri-jan-dhan-yojna-pmjdy.html
https://www.godigit.com/guides/government-schemes/pradhan-mantri-jan-dhan-yojana-pmjdy








